Romania
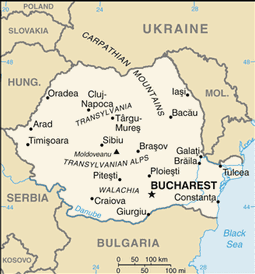 Romania is country of Europe located in east Europe.
Romania is country of Europe located in east Europe.
Details
| Official Name: | Republic of Romania |
| Capital: | Bucharest |
| Total area: | 238 391 km2 |
| GDP per capita: | $42,408 |
| Native Language: | Romanian |
| Government: | Unitary Semi-presidential republic |
| Population: | 20,121,641 |
| Major Religion: | Orthodox Christianity |
| Monetary Unit: | Romanian leu (RON) |
Romania, in southeast Europe, is mountainous in the north while the main feature in the south is the vast Danube valley. The river forms a delta as it approaches the Black Sea, which is a wildlife reserve for countless native and migratory birds.
The Romanian parliament consists of two chambers, the Senat (Senate) and the Camera Deputaţilor (Chamber of Deputies). The members of both are chosen in elections held every four years.
Ethnically, the population is 90% Romanian and 7% Hungarian. The Romanian language, like a number of others in southern Europe, is directly descended from Latin, although Romania is separated from other Romance-language countries by Slav speakers. Romania has considerable natural resources – oil, natural gas, coal, iron, copper and bauxite. Metal-working, petrochemicals and mechanical engineering are the main industries.
Romanian speciality dishes include grilled meatballs, meat wrapped in cabbage leaves, pork stew with garlic and onions and doughnuts made with cream and cheese.
The spine-chilling tale of Dracula was inspired by the 15th century Romanian Count Vlad Dracul whose son was famous in wartime for impaling captured enemies. Less notorious Romanians include the writer Eugene Ionesco, the gymnast Nadia Comăneci and the composer George Enescu.
Economy
With a GDP of around $274 billion in 2012 and a GDP per capita (PPP) of $12,800 for the year 2012, Romania is an upper-middle income country economy and has been part of the European Union since 1 January 2007.
After the communist regime was overthrown in late 1989, the country experienced a decade of economic instability and decline, led in part by an obsolete industrial base and a lack of structural reform. From 2000 onwards, however, the Romanian economy was transformed into one of relative macroeconomic stability, characterised by high growth, low unemployment and declining inflation. In 2006, according to the Romanian Statistics Office, GDP growth in real terms was recorded at 7.7%, one of the highest rates in Europe.
Growth dampened to 6.1% in 2007, but was expected to exceed 8% in 2008 because of a high production forecast in agriculture (30–50% higher than in 2007). The GDP grew by 8.9% in the first nine months of 2008, but growth fell to 2.9% in the fourth quarter and stood at 7.1% for the whole 2008 because of the financial crisis. Thereafter, the country fell into a recession in 2009 and 2010, where the GDP contracted −7.1% and −1.3% respectively. However, the GDP grew again by 2.2% in 2011 and 0.7% in 2012. It is estimated the GDP will continue to grow by 1.6% in 2013 and 2.2% in 2014.
Immigration and residency
If you are interested in moving to the countries, either with a residence permit or by acquiring a citizenship, please contact us, and also get acquainted with the relevant migration documents.